Lab #15: Collisions in two dimensions
Dahlia - Ariel - Carlos
19-Oct-2016
The purpose of the lab#15 is when looking at a two dimensional collision, student can determine if momentum are conserved or not.
I. Set up:
There were 2 plastic balls and 1 steel ball. ( 2 ball collides at a time)
There was also a glass board where 2 ball collide.
There was a phone recorded the collision and transfer it to log pro.
And I used log pro to record the position and velocity of 2 balls
II. Analysis.
1. Part 1: a steel ball collided with a plastic ball
Because the steel ball was much heavier than the plastic ball, the velocity of the steel ball before and after the collision did not changed so much.
The velocity before and after the collision were the slopes of the graph.
The velocity of the plastic ball was changed really clearly
The velocity of the plastic ball before the collision was 0, and it raised up to 0.1532 m/s after the collision.
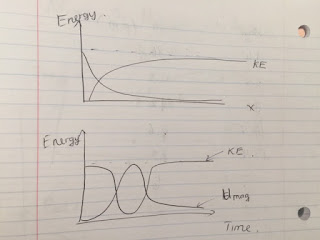
by the conservation of momentum, the graph of momentum had to be a straight line parallel with x-axis, but my graph was so weird, so I do not bring it up here; However, ideal, the momentum had to be a constant.
Then, I graph the center mass of 2 balls
This was x-cm and y-cm vs t. They were raised at a line. the slope of them were 0.09 and 0.24
Finally, I graphed the velocity of x-cm and y-cm vs time.
This graph was not great, but I could predict that the velocity of center mass looked like a Cos shape.
2. Part 2: 2 plastic balls
Now, I did the same progress with 2 plastic balls
Because 2 ball had the same of mass, the position at the begin and after collision was change clearly; thus, the velocity at before and after were also changed. from the slope of graph, I could see that the velocity at the beginning was 0.3 m/s and the velocity after the collision was 0.09 m/s
In the same story, the velocity of the other ball had also changed. the velocity at the beginning was 0- at rest, and the velocity after the collision was 0.1579 m/s
The same with part 1, the momentum of 2 balls had to be a constant
Now, I graph the center mass of 2 balls
The slopes of 2 balls were 0.13 and 0.10. Because the mass of 2 balls were similar, thus the direction of the center mass were also parallel.
Finally, I graph the velocity of center mass
It was not great at all.
III. Conclusion
From this experiment, I can use a video of a collision, analysis it by log pro, and conclude if the momentum was conserved or not. in my lab, the momentum was not conserved, but ideally, the momentum has to be conserved.
I. Set up:
There were 2 plastic balls and 1 steel ball. ( 2 ball collides at a time)
There was also a glass board where 2 ball collide.
There was a phone recorded the collision and transfer it to log pro.
And I used log pro to record the position and velocity of 2 balls
II. Analysis.
1. Part 1: a steel ball collided with a plastic ball
Because the steel ball was much heavier than the plastic ball, the velocity of the steel ball before and after the collision did not changed so much.
The velocity before and after the collision were the slopes of the graph.
The velocity of the plastic ball was changed really clearly
The velocity of the plastic ball before the collision was 0, and it raised up to 0.1532 m/s after the collision.
by the conservation of momentum, the graph of momentum had to be a straight line parallel with x-axis, but my graph was so weird, so I do not bring it up here; However, ideal, the momentum had to be a constant.
Then, I graph the center mass of 2 balls
This was x-cm and y-cm vs t. They were raised at a line. the slope of them were 0.09 and 0.24
Finally, I graphed the velocity of x-cm and y-cm vs time.
This graph was not great, but I could predict that the velocity of center mass looked like a Cos shape.
2. Part 2: 2 plastic balls
Now, I did the same progress with 2 plastic balls
Because 2 ball had the same of mass, the position at the begin and after collision was change clearly; thus, the velocity at before and after were also changed. from the slope of graph, I could see that the velocity at the beginning was 0.3 m/s and the velocity after the collision was 0.09 m/s
In the same story, the velocity of the other ball had also changed. the velocity at the beginning was 0- at rest, and the velocity after the collision was 0.1579 m/s
The same with part 1, the momentum of 2 balls had to be a constant
Now, I graph the center mass of 2 balls
The slopes of 2 balls were 0.13 and 0.10. Because the mass of 2 balls were similar, thus the direction of the center mass were also parallel.
Finally, I graph the velocity of center mass
It was not great at all.
III. Conclusion
From this experiment, I can use a video of a collision, analysis it by log pro, and conclude if the momentum was conserved or not. in my lab, the momentum was not conserved, but ideally, the momentum has to be conserved.